Cloud Computing: Unleashing the Power of Digital Transformation
Introduction
In the fast-paced digital age, businesses and individuals alike seek scalable and efficient solutions to store, manage, and access data. Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing the way we store, process, and share information. In this blog, we will explore the world of cloud computing, its fundamental concepts, diverse models, and the profound impact it has had on various industries and daily life.
Understanding Cloud Computing
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers, cloud computing enables users to access a vast network of remote servers hosted in data centers. These servers store and manage data, applications, and services, making them accessible from virtually anywhere with an internet connection.
Key Concepts of Cloud Computing
On-Demand Self-Service: Users can access cloud computing resources on-demand, without the need for human intervention from the service provider.
Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the internet and can be used from various devices, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
Resource Pooling: Cloud providers pool resources such as storage, processing power, and memory to serve multiple customers efficiently.
Rapid Elasticity: Cloud resources can scale up or down based on demand, allowing users to adjust their computing resources dynamically.
Measured Service: Cloud computing services are metered, enabling users to pay only for the resources they consume.
Cloud Computing Models
There are three primary cloud computing models:
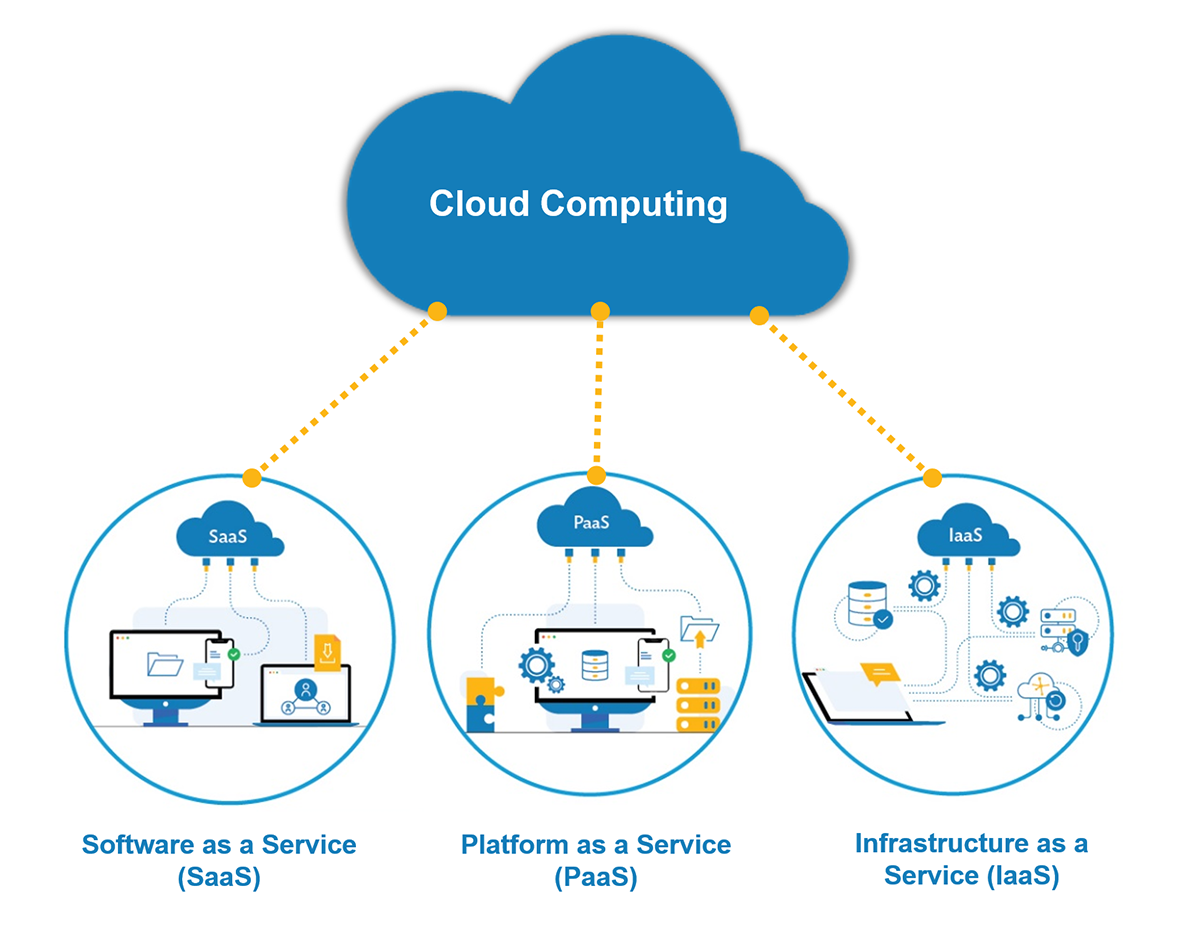
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking components, allowing them to run their applications without managing physical hardware.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform with pre-configured development tools and services, enabling users to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers fully functional applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, manage, and maintain software on their devices.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The adoption of cloud computing brings numerous advantages:
Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their resources up or down according to demand, reducing costs and ensuring optimal performance.
Cost-Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront capital investment in hardware, allowing businesses to pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Flexibility and Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
Security: Reputable cloud providers implement robust security measures, protecting data from threats and unauthorized access.
Applications of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing's impact is evident across various sectors:
1. Business and Enterprise: Cloud computing empowers businesses with data storage, collaboration tools, and software applications, enabling streamlined operations and efficient workflows.
2. Education: Cloud-based learning management systems and online collaboration tools facilitate remote education and distance learning.
3. Healthcare: Cloud-based electronic health records improve patient care, data accessibility, and interoperability among healthcare providers.
4. Entertainment and Media: Streaming services and cloud-based content delivery networks revolutionize the way we consume media.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, cloud computing faces challenges:
Data Security and Privacy: Storing data on remote servers raises concerns about data security and privacy, necessitating robust encryption and compliance with regulations.
Vendor Lock-In: Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be complex, leading to concerns about vendor lock-in.
Internet Dependency: Cloud computing relies on a stable internet connection, which can be a limitation in areas with limited connectivity.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an essential pillar of the digital transformation era, shaping the way we store, access, and process information. With its scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility, cloud computing has enabled businesses and individuals to embrace a new paradigm of computing. As cloud technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly catalyze further innovation, drive efficiency, and empower us to harness the vast potential of the digital world. As we embrace the cloud's potential, it is essential to address security concerns and ensure responsible data management, creating a future where the cloud remains a catalyst for progress and inclusivity.
Comments
Post a Comment